See Our Latest Blogs
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur
A Complete Walkthrough to the Retirement Income
Master Your Retirement: Step-by-Step Guidance from Planning to Prosperity – Part 1 to 9
Planning for retirement is one of the most important financial decisions you’ll make in your lifetime. Understanding how to generate reliable income streams during your retirement years is crucial for maintaining the lifestyle you desire. In this guide, we’ll walk you through the essential steps to ensure you have the income you need, when you need it.
This guide is designed for those of all ages and stages of life. Whether you’re just starting your career, nearing retirement, or already retired, the principles of generating retirement income remain the same. Let’s dive into the key elements that can help you secure your future.
Topics
1. Setting Retirement Goals
2. The True Cost of Retirement
3. Understanding Your Income Needs
4. Non-Investment Income Sources
5. Investment Income Sources
6. Strategies to Protect Your Retirement Income
7. Planning for Longevity and Inflation
8. Creating a Retirement Income Plan
9. Case Studies
10. Conclusion
1. Setting Retirement Goals
Before diving into how to generate retirement income, it’s essential to define what your retirement goals are. Understanding your goals will help shape your income strategy. Here are some key questions to consider:
· What kind of lifestyle do you want? Are you looking to maintain your current lifestyle, improve it, or focus on increasing wealth for future generations?
· How much income will you need each month? Consider your living expenses, discretionary spending (like travel and entertainment), and savings for emergencies.
· What is your retirement age? The earlier you retire, the longer your money will need to last.
Types of Goals:
· Lifestyle Maintenance: Focus on covering basic living expenses and maintaining your current lifestyle.
· Legacy Planning: Plan to leave wealth to family, charities, or causes you care about.
· Wealth Growth: Continue to build wealth during retirement for long-term security.

2. The True Cost of Retirement
The cost of retirement isn’t just about daily expenses. Several factors can influence your budget:
· Non-Discretionary Costs: These are unavoidable expenses, such as housing, taxes, utilities, and healthcare.
· Discretionary Costs: These are optional expenses like travel, hobbies, and entertainment. While you can control these, they significantly enhance your quality of life in retirement.
· Healthcare Costs: As you age, healthcare needs tend to increase. Be sure to plan for these costs as they can become substantial.
·
Table 1: Estimating Your Retirement Costs
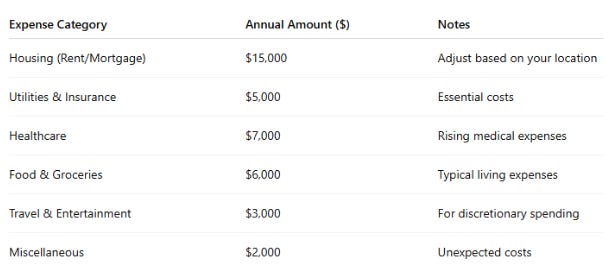
3. Understanding Your Income Needs
Once you’ve calculated your expenses, it’s time to think about how to fund your retirement. This involves understanding how much income you’ll need on a monthly or annual basis and from where that income will come. The key is balancing non-investment income (pensions, government benefits) with investment income (stocks, bonds, real estate).
How to Calculate Your Income Needs:
1. Estimate Your Annual Expenses: Add up your living and discretionary costs.
2. Account for Inflation: Over time, inflation will erode the purchasing power of your money. Plan for a 2–3% inflation rate.
3. Factor in Healthcare Costs: Ensure you have coverage for both routine and emergency medical needs.
4. Non-Investment Income Sources
a. Government Pensions: Canada Pension Plan (CPP)
The Canada Pension Plan (CPP) provides a reliable source of income for Canadians who have contributed during their working years. The amount you receive depends on your earnings during your working life and the age at which you begin receiving your benefits.
· Start Age: You can begin receiving CPP at age 60, but waiting until age 65 or later may result in higher monthly payments.
· How Much You’ll Receive: There are online calculators available to estimate your CPP benefits based on your work history.
b. Work Pensions
Employer pensions (such as Defined Benefit or Defined Contribution plans) can be a significant source of retirement income. Ensure you understand:
· How much you will receive each month.
· Whether your pension increases or decreases over time.
c. Rental Income from Real Estate
If you have invested in property, the rental income can be a steady source of cash flow in retirement. However, this income can be influenced by market conditions, so it’s important to consider the liquidity of your real estate holdings.
d. Salary from Part-Time Work
Many retirees opt to work part-time. While this may not be your primary income, it can provide additional cash flow and help ease the transition into full retirement.
5. Investment Income Sources
In addition to non-investment income, you will likely need to rely on investment income to cover the remaining expenses. Investment income can come from a variety of sources, including:
a. Bonds
Bonds provide regular coupon payments, making them an excellent choice for retirees who need consistent cash flow. However, bond yields tend to be lower than stocks and may not always keep up with inflation.
b. Stock Dividends
Many stocks pay dividends to shareholders. These dividends can be a reliable source of income in retirement. A diversified portfolio of dividend-paying stocks can help you maintain a steady income stream.
c. Real Estate Investment Trusts (REITs)
REITs allow you to invest in a diversified portfolio of real estate properties without owning physical property. They are known for offering high dividend yields and can be an attractive source of income for retirees.
d. Selling Stocks for Cash Flow
Strategically selling stocks from your portfolio can provide the necessary cash flow to cover your retirement expenses. This method is known as "homegrown dividends."

6. Strategies to Protect Your Retirement Income
To ensure your retirement income lasts for the long term, you must focus on protecting your income streams. Here are a few strategies:
a. Diversification
Ensure your portfolio is well-diversified across asset classes (stocks, bonds, real estate). This reduces the risk of having all your income dependent on one source.
b. Creating a Balanced Portfolio
Create a portfolio that includes both growth and income-generating assets. While bonds provide stability, stocks offer long-term growth potential, and REITs provide steady income.
c. Annuities
An annuity can provide a guaranteed income for life, helping protect you from outliving your assets. However, annuities come with their own set of pros and cons, so be sure to understand the terms.
7. Planning for Longevity and Inflation
As people are living longer, it’s important to plan for longevity risk—the possibility that you’ll outlive your savings. Additionally, inflation can erode your purchasing power, so it’s crucial to factor in inflation when calculating your retirement needs.
· Longevity: Plan for at least 25–30 years of retirement income.
· Inflation: Consider investments that tend to outpace inflation, such as stocks, real estate, and inflation-protected bonds.
8. Creating a Retirement Income Plan
Once you’ve gathered all the necessary information, it’s time to create a retirement income plan. This plan should:
1. Outline your income sources (government, pensions, investments).
2. Estimate your monthly and annual retirement expenses.
3. Include an emergency fund for unexpected costs (healthcare, home repairs).
4. Take into account the need for flexibility as your needs may change over time.
9. Case Studies: Real-World Scenarios
Case Study 1: Young Professional, Early Retirement Planning
Emma, 35 years old, is just starting her retirement savings journey. She focuses on contributing regularly to her RRSP and Tax-Free Savings Account (TFSA). She expects her retirement expenses to be around $40,000 per year. By age 60, Emma anticipates having a mix of RRSP withdrawals, pension income, and investment income.
Case Study 2: Pre-Retiree, Nearing Retirement
John, 55 years old, is nearing retirement with an established work pension and real estate holdings. He plans to use his pension income and rental income to cover 70% of his retirement expenses, with the remaining 30% coming from his investment portfolio.
10. Conclusion
Retirement income planning is a critical part of achieving a comfortable and secure retirement. By setting clear goals, understanding your expenses, and creating a balanced income strategy, you can enjoy the retirement you deserve.
To get personalized advice on your retirement, schedule a consultation.

